Unveiling the Health Implications of Metal Implants
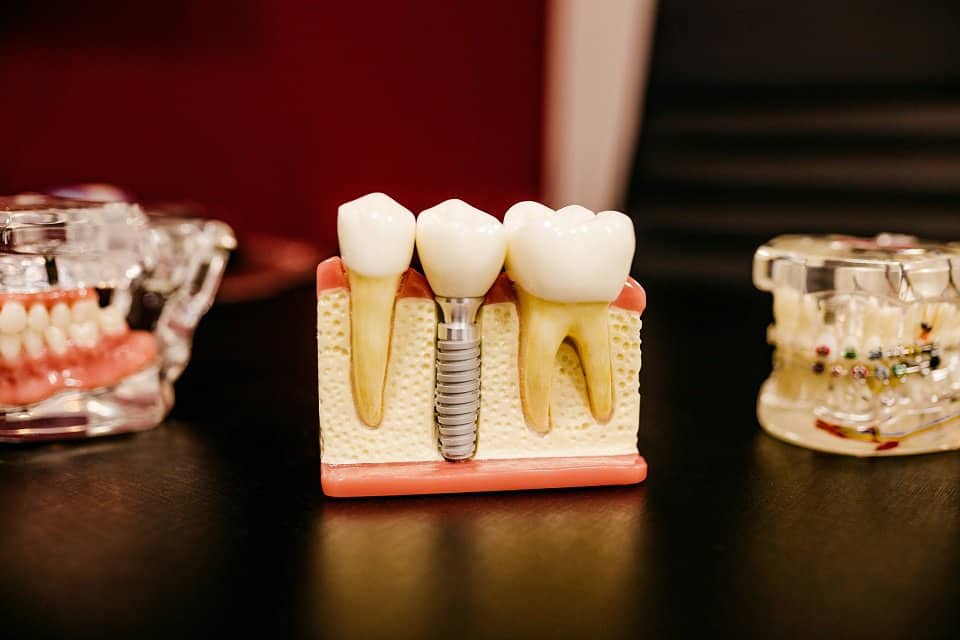
In the realm of modern medicine, metal implants, from dental amalgams to orthopedic screws, have become commonplace solutions to a myriad of health issues. However, recent findings by Dr. Scott A. Schroeder and the exploration of patient experiences are shedding light on the potential deleterious effects these metal implants can have on our health. This article delves into three significant health concerns associated with metal implants: toxic mercury vapors from amalgam fillings, mitochondrial dysfunction, and the phenomenon of galvanism, unraveling the complex interactions between our bodies and these foreign materials.
Mercury Vapors and Neurological Issues
Dental amalgam fillings, a longstanding solution for tooth decay, are known to release mercury vapors. Mercury, even in trace amounts, can lead to neurological issues, including memory loss, fatigue, and tremors. The concern is not just hypothetical; numerous studies and patient testimonials have highlighted the correlation between amalgam fillings and deteriorating neurological health. Dr. Schroeder’s insights into patient reactions post-surgery highlight the urgent need to reassess the use of amalgam fillings, especially given their potential to release toxic mercury into our bodies.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: The Energy Crisis
Mitochondria, the powerhouses of our cells, are sensitive to the toxic effects of heavy metals. Exposure to metals like nickel, found in certain implants, can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, manifesting as chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), muscle weakness, and even neurological disorders. This dysfunction arises from the metals’ interference with the mitochondria’s ability to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell, leading to an energy crisis within the body.
Galvanism: A Silent Culprit
Galvanism occurs when dissimilar metals (for example, titanium implants in the foot and amalgam dental fillings) are present within the body’s saline environment, creating a battery-like effect. This galvanic action can enhance the release of metal ions into the body, exacerbating toxicity and leading to symptoms such as chronic pain, paralysis, and fibromyalgia. Dr. Schroeder’s investigations have revealed dramatic health improvements in patients once one source of galvanism, such as amalgam fillings, is removed.
Transformative Relief: The Impact of Addressing Metal Sensitivities
Dr. Scott A. Schroeder’s clinical practice has illuminated the stark reality of metal sensitivities and their capability to invoke debilitating symptoms in patients, symptoms that remarkably diminish or altogether disappear with the strategic exchange of one metal for another in their bodies. He shares compelling narratives, such as that of an engineer plagued by daily paralyzing episodes, which were significantly mitigated upon the removal of specific metallic implants. This particular patient, once facing a grim future confined to a wheelchair, experienced a dramatic health reversal following the extraction of nickel-containing screws and the replacement of palladium-laden dental crowns. These cases highlight not only the critical impact of metal sensitivities on an individual’s health but also the transformative potential of identifying and addressing these sensitivities. Through interventions like removing or swapping out reactive metals, patients have seen substantial improvements, emphasizing the pivotal role that understanding and managing metal sensitivities plays in restoring health and enhancing the quality of life.
The Path to Healing
Recognizing the symptoms associated with metal sensitivities and galvanic reactions is crucial. For many, the solution lies in the removal of one source of galvanism, such as amalgam fillings, to alleviate the immediate source of toxicity. However, for comprehensive healing, addressing the residual heavy metal toxicity is paramount.
Here, the Detoxination® protocol offers a beacon of hope. Designed to liberate and remove heavy metals from the body, this protocol can significantly mitigate the risk of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, paving the way for cellular healing and restoration of energy levels. Detoxination, with its foundation in sauna therapy and supported by the pharmacokinetics of niacin, presents a holistic approach to tackling the underlying causes of heavy metal toxicity.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of our interactions with metal implants, the work of Dr. Scott A. Schroeder and the growing body of research on metal sensitivities serve as a crucial reminder of the need for personalized healthcare approaches. By understanding the risks associated with metal implants and advocating for safer alternatives, we can safeguard our health and well-being in an increasingly metal-dependent world. The journey towards healing begins with awareness, and for those affected, Detoxination offers a scientifically backed path to recovery.
Watch an Interview with Dr. Scott A. Schroeder
About the MELISA test Dr. Schroeder mentions:
The MELISA (Memory Lymphocyte Immunostimulation Assay) test is a clinically validated method used to detect metal hypersensitivity, particularly useful for individuals with metal implants or dental restorations. This test is based on measuring the immune system’s response to various metals by assessing lymphocyte reactivity. Here are key points about the MELISA testing for metal sensitivities:
- Validation and Reliability: The MELISA test was validated on 250 patients in 2003, demonstrating its reproducibility, sensitivity, specificity, and reliability for detecting metal sensitivity. Further validation on a larger group of patients was published in 2016, and a 2021 university study noted the “significant benefits of MELISA testing.”
- Applications: MELISA testing has been particularly highlighted for its relevance in patients with failed orthopedic implants and those requiring orthopedic implant surgery. It helps identify metal hypersensitivity and pro-inflammatory cytokine production, which may contribute to implant failure or adverse reactions.
- Metal Hypersensitivity: The test can diagnose hypersensitivity to a wide range of metals, which is crucial for patients with or considering metal-containing implants or dental restorations. Understanding individual sensitivities can guide more personalized and safer healthcare decisions.
- Clinical Benefits: A study emphasized the clinical benefit of the MELISA test in minimizing or eliminating health problems in patients with confirmed hypersensitivity to metals used for tissue replacements, primarily focusing on titanium and fifteen other metals.
- Wider Acceptance: Despite its benefits, it’s noted that the FDA has not approved or sanctioned the test, and most health plans do not cover the cost. However, the data suggest that the MELISA test is a valuable tool for detecting metal sensitivities, contributing to improved patient care.
In summary, the MELISA test represents a significant advancement in identifying and managing metal hypersensitivity, especially relevant for individuals with or considering metal-containing medical implants. It underscores the importance of recognizing metal sensitivities in the context of patient health and implant success, offering a pathway to more tailored and safer treatment options.
To get tested with MELISA for metal sensitivities, follow these steps:
- Find a Provider: Locate a healthcare provider or a clinic that offers MELISA testing. The MELISA website often provides a directory of laboratories and clinicians around the world who are trained to administer the test.
- Consultation: Schedule a consultation with the healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms and the need for MELISA testing. This is important to ensure the test is appropriate for your specific concerns and to understand what metals or allergens should be included in the test.
- Blood Sample Collection: The MELISA test requires a blood sample, which is usually drawn at the healthcare provider’s office or a designated laboratory. The collected blood sample is then sent to a MELISA-accredited laboratory for analysis.
- Testing: In the laboratory, your white blood cells (lymphocytes) are isolated and exposed to various metals or allergens to see if there is a specific immune response. The test measures lymphocyte proliferation in response to these substances, which indicates a hypersensitivity or allergic reaction.
- Results and Consultation: Once the results are available, typically within a few weeks, schedule a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss the findings. The results will indicate if you have a sensitivity to any of the tested metals, which can guide further treatment or avoidance strategies.
- Follow-up Actions: Based on the test results, your healthcare provider may recommend specific actions, such as removing or avoiding the offending metals, dietary changes, or other interventions to manage your metal sensitivities.
It’s important to work with a healthcare provider familiar with MELISA testing and metal sensitivities to ensure accurate interpretation of the results and to receive appropriate guidance on managing any identified sensitivities.
Daniel Root is the leading expert, practitioner, and trainer of Detoxination®. He is the son of the world renowned expert in human detoxification of heavy metals, synthetic/man-made chemicals, and radiation, Dr. David E. Root.
Dan and his father authored Sauna Detoxification Using Niacin that sells thousands of copies worldwide.
He was co-host of a weekly radio program, The Get Detoxinated! Show on KSAC 105.5 FM.
Dan is the CEO of Detoxination Wellness Centers, a dba of Sabre Hawk, LLC.
He has been an entrepreneur in the Information Technology field since 1989, and is the adoptive father of 3 biological sisters.
Dan served on the Board of Sierra Adoption Services for 6 years. He lives with his wife, Suzy, and their youngest daughter in Sacramento, California.
 Click here to learn more about our Testimonials and Results Disclaimer
Click here to learn more about our Testimonials and Results Disclaimer
Disclaimer: Information on this web site is provided for informational purposes only. The information is a result of years of practice experience by the authors. This information is not intended as a substitute for the advice provided by your physician or other healthcare professional or any information contained on or in any product label or packaging. Do not use the information on this web site for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease, or prescribing medication or other treatment. Always speak with your physician or other healthcare professional before taking any medication or nutritional, herbal or homeopathic supplement, or using any treatment for a health problem. If you have or suspect that you have a medical problem, contact your health care provider promptly. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking professional advice because of something you have read on this web site. Information provided on this web site and the use of any products or services purchased from our web site by you DOES NOT create a doctor-patient relationship between you and any of the physicians affiliated with our web site. Information and statements regarding dietary supplements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.




You must be logged in to post a comment.